? Introduction to GraphQL + React + Java + Astra DB
50 minutes, Beginner/Intermediate, Start Building
Both a simple graphQL enabled ReactJS app built using create-react-app AND a simple Java backend graphQL service built with Spring Initializr and using The Netflix DGS framework PLUS Astra DB hooked up and ready to rock! ?
This is a companion to our Netflix Clone using Astra DB and GraphQL workshop and is essentially a “prologue” to that content. Once complete, feel free to to go deploy a Netflix clone using what you learned here.
Finally, this content uses React/JS concepts. If you are not familiar with those or need a refresher, take a look HERE to get up to date.
The materials have been built by the DataStax developer advocates team.
? Objectives
- An overview of what GraphQL is and what makes it cool
- What differs between GraphQL, REST, other APIs, and their pros/cons
- Hands-on examples of GraphQL queries and mutations
- How to build GraphQL APIs for mobile and web applications
- Setting up your Astra DB to store application data via GraphQL
ℹ️ Frequently asked questions ℹ️
- Can I run the workshop on my computer?
There is nothing preventing you from running the workshop on your own machine.
If you do so, you will need
- node 15 and npm 7 or later
- netlify-cli (use “npm install -g netlify-cli”)
You will have to adapt commands and paths based on your environment and install the dependencies by yourself. We won’t provide support to keep on track with schedule. However, we will do our best to give you the info you need to be successful. This is considered a more advanced path to take.
- What other prerequisites are there?
- You will need a github account
- You will need an Astra DB account, but we’ll work through that in the exercises
- Use Chrome or Firefox for the best experience.
- Do I need to pay for anything for this workshop?
- No. All tools and services we provide here are FREE.
- Will I get a certificate if I attend this workshop?
Attending the session is not enough. You can earn yourself a nice badge to brag about if you complete all of the homework.
Materials for the Session
It doesn’t matter if you join our workshop live or you prefer to do at your own pace, we have you covered. In this repository, you’ll find everything you need for this workshop:
Homework
Don’t forget to complete your upgrade and get your verified skill badge! Finish and submit your homework!
- Complete the practice steps from this repository as described below through step 9
- Insert (mutate) a show or genre of your choice in the database.
- Make a single screenshot of the React app with all of the working Astra DB sections
- Submit your homework here
That’s it, you are done! Expect an email within about a week!
Let’s start
Extra resources
graphql.org – The first place to learn about GraphQL
The Netflix DGS framework Tutorial – Java/Spring GraphQL backend (used to generate this code)
Spring Initializr – Used in the ^above tutorial to generate the Java/Spring backend starter
GraphiQL – GraphQL IDE included with The Netflix DGS Framework
Apollo client – Awesome GraphQL client for React/JS (not used here, but really solid, Netflix uses this)
Top 7 GraphQL IDEs – A nice collection of cool GraphQL IDEs to use
create-react-app tutorial – Create a React app from scratch (used to generate this code)
A Beginner’s Guide to GraphQL – Ali Spittel’s really awesome GraphQL starter video
Part 1 – DB Setup & Data Ingest
1. Login or Register to AstraDB and create database
ASTRADB is the simplest way to run Cassandra with zero operations at all – just push the button and get your cluster. No credit card required, FREE for roughly 5M writes, 30M reads, 40GB storage monthly – sufficient to run small production workloads.
✅ Step 1a: Click the button to login or register with Datastax. You can use your Github, Google accounts or register with an email.
Make sure to chose a password with minimum 8 characters, containing upper and lowercase letters, at least one number and special character
Use the following values when creating the database
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| database name | netflix_workshop_db |
| keyspace | netflix_keyspace |
| Cloud Provider | Use the one you like, click a cloud provider logo, pick an Area in the list and finally pick a region. |
You can technically use whatever you want and update the code to reflect the keyspace. This is really to get you on a happy path for the first run.
You will see your new database pending OR initializing in the Dashboard.
The status will change to Active when the database is ready, this will only take 2-3 minutes. You will also receive an email when it is ready.
2. Create a security token
✅ Step 2a: Create a token for your app to use in the settings screen. Use “Database Administrator” permission.
✅ Step 2b: Copy the token value (eg AstraCS:KDfdKeNREyWQvDpDrBqwBsUB:ec80667c....) in your clipboard and save the CSV, this value would not be provided afterward.
?️ Expected output
3. Launch Gitpod
Gitpod is an 100% online IDE based on VS Code. To initialize your environment simply click on the button below (CTRL + Click to open in new tab) You will be asked for you github account, as needed.
This will startup your demo environment. Be patient, it will take a couple minutes as everything loads up.
You may be asked if it’s OK to launch a new tab (for the GraphiQL IDE that will be used subsequently. Click on Open to make sure the new tab opens as shown below.
4. Experiment with GraphiQL
It just so happens that The Netflix DGS framework comes with GraphiQL already integrated and ready for use. This is a wonderful tool you can use to explore graphQL queries and mutations. Let’s experiement with this now!
Here’s the schema defined in our java backend per graphql-backend-examples/src/main/resources/schema/schema.graphqls/schema.graphqls
type Query {
shows(titleFilter: String): [Show]
genres(labelFilter: String): [Genre]
}
type Show {
title: String
releaseYear: Int
}
type Genre {
value: String!
}
Something to point out here is there is no database just yet. We are powering the graphQL schema via the back-end Java application and the graphQL data is completely hardcoded. Take a look at both ShowsDatafetcher.java and GenresDatafetcher.java located in graphql-backend-examples/src/main/java/com/example/demo to find the simple implementations using DGS annotations @DgsComponent and @DgsQuery.
Now, let’s try out some graphQL queries
Plug these into the GraphiQL IDE that launched into a new tab from GitPod.
query justTitle {
shows {
title
}
}
query withReleaseYear {
shows {
title
releaseYear
}
}
query getOneShow {
shows (titleFilter: "Ozark") {
title
releaseYear
}
}
query ShowsAndGenres {
shows {
title
releaseYear
}
genres {
value
}
}
5. Start up React
Ok, so we’ve played a bit with some graphQL queries on the backend and looked at how a basic schema works, but how do we hook this into our React JS app?
First, we need to run a couple commands to get things setup
In your GitPod IDE navigate to the workshop-intro-to-graphql/graphql-client-examples terminal on the bottom right (it should already be open for you).
✅ Execute the following command
npm install -g netlify-cli
This will install the Netlify CLI (command line interface) which our React/JS app uses in conjunction with the serverless functions we’ve setup to talk to our graphQL endpoints.
✅ Then, execute
netlify dev
This will start the React/JS application and display results from both the Shows and Genres graphQL queries and endpoints we were just experimenting with.
Compare javascript code to our graphQL queries from above
If you take a look at both getShowsBackend.js and getGenresBackend.js located in graphql-client-examples/functions you should notice that both use the same exact graphQL queries that we used above.
const query = `
query getAllShows {
shows {
title
releaseYear
}
}
`
const query = `
query getAllGenres {
genres {
value
}
}
`
All of the javascript wrapped around these is simply there to call the graphQL endpoint with the given query and pass the responseBody back to the calling function.
Now for the cool part
Take a look at Shows.js and Genres.js located in graphql-client-examples/src/components/Shows.js. In both cases they use React state, gqlResult
const [gqlResult, setGqlResult] = useState(null)
to receive the responseBody from from our graphQL queries, set the React state, and inject the values dyanmically into the DOM. Check out the following javascript snippet from Shows.js.
// Asynchronously fetch any "shows" graphQL data from the Java backend
// using the getShowsAstra serverless function to call out to the
// Netflix DGS Java graphQL endpoint
const response = await fetch("/.netlify/functions/getShowsBackend", {
method: "POST",
})
const responseBody = await response.json()
setGqlResult(responseBody) // on reponse set our graphQL result state
Notice how the fields (title, releaseYear) match our graphQL Shows schema exactly.
// Finally, if all other checks pass get the data
// from the payload via gqlResult state and inject it into the DOM
// Notice how the payload example below and the fields "title" and "releaseYear" match exactly
// {"data":{"shows":[{"title":"Stranger Things","releaseYear":2016},{"title":"Ozark","releaseYear":2017}...
return gqlResult.data.shows.map(({ title, releaseYear }) => (
<div key={title}>
<p>
{title}: {releaseYear}
</p>
</div>
));
Notice how the field (value) matches our graphQL Genres schema exactly.
// Finally, if all other checks pass get the data
// from the payload via gqlResult state and inject it into the DOM
// Notice how the payload example below and the fields "title" and "releaseYear" match exactly
// {"data":{"genres":[{"value":"Action"},{"value":"Anime"}...
return gqlResult.data.genres.map(({ value }) => (
<div key={value}>
<p>
{value}
</p>
</div>
));
6. Hook up the data layer with Astra DB
Ok, let’s take this a step further and hook our app up to a data layer. As this point you should have already created your Astra DB database. Follow the instructions below to launch the GraphQL Playground provided in Astra
✅ Step 6a: Open GraphQL Playground by
- Click on your active database
- Click
ConnectTAB - Click
GRAPHQL API - Click link to your playground.
Note that values in the picture do no reflect the database name
netflix_workshop_db, reason is we do not reproduce every picture each time
✅ Step 6b: In GraphQL Playground, Populate HTTP HEADER variable x-cassandra-token on the bottom of the page with your token as shown below
✅ Ensure you have the graphql-schema tab selected for this step
✅ Step 6c: In GraphQL Playground, create a table with the following mutation, making sure to replace netflix_keyspace if you used a different name:
- Copy the following mutation on the left panel
mutation {
reference_list: createTable(
keyspaceName:"netflix_keyspace",
tableName:"reference_list",
ifNotExists:true
partitionKeys: [
{ name: "label", type: {basic: TEXT} }
]
clusteringKeys: [
{ name: "value", type: {basic: TEXT}, order: "ASC" }
]
)
}
- Use the arrow in the middle of the screen to execute the query
7. Insert data in the Table with GraphQL
✅ Step 7a: In graphQL playground, change tab to now use graphql. Edit the end of the URl to change from system to the name of your keyspace: netflix_keyspace
✅ Step 7b: Populate HTTP HEADER variable x-cassandra-token on the bottom of the page with your token as shown below (again !! yes this is not the same tab)
✅ Step 7c: In GraphQL Playground,populate the reference_list table with the following values
- Copy the following mutation on the left panel
mutation insertGenres {
action: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Action"}) {
value{value}
}
anime: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Anime"}) {
value{value}
}
award: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Award-Winning"}) {
value{value}
}
children: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Children & Family"}) {
value{value}
}
comedies: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Comedies"}) {
value{value}
}
documentaries: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Documentaries"}) {
value{value}
}
drama: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Dramas"}) {
value{value}
}
fantasy: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Fantasy"}) {
value{value}
}
french: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"French"}) {
value{value}
}
horror: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Horror"}) {
value{value}
}
independent: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Independent"}) {
value{value}
}
music: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Music & Musicals"}) {
value{value}
}
romance: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Romance"}) {
value{value}
}
scifi: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Sci-Fi"}) {
value{value}
}
thriller: insertreference_list(value: {label:"genre", value:"Thriller"}) {
value{value}
}
}
- Use the arrow in the middle of the screen to execute the query
8. Retrieving list of values
✅ Step 8a: In GraphQL Playground, not changing tab (yeah) list values from the table with the following query.
query getAllGenre {
reference_list (value: {label:"genre"}) {
values {
value
}
}
}
9. Hook the database up to our React/JS app
So, you just created a table, inserted (mutated) some rows into the table, and then retrieved all of the genres with the “getAllGenre” query using the GraphQL Playground provided as part of Astra DB. Now, let’s hook our client up to our Astra DB graphQL endpiont and render the results to our website with React.
✅ Step 9a: Configure database credentials
In your GitPod IDE navigate to the workshop-intro-to-graphql/graphql-client-examples terminal on the bottom right (it should already be open for you). This is running your nodejs/React app.
✅ Execute the following command in your terminal to stop the React app
You will need to hold the control button and the letter C at the same time
CTRL-C
✅ Now execute the following command to configure the database
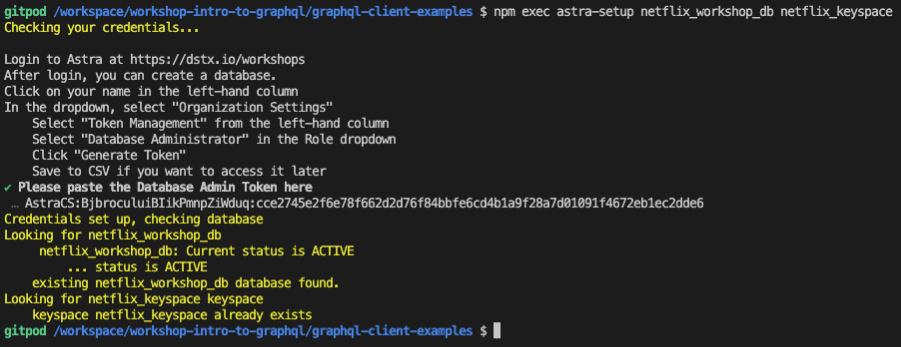
Note that this does require Node 15 and NPM 7 to work. You can install a node version manager like nvm or n to use multiple versions on your system. If you are using GitPod this should simply work since we pre-installed all of the dependcies for you.
npm exec astra-setup netflix_workshop_db netflix_keyspace
You will be asked to: Please paste the Database Admin Token here so copy over the Token you saved earlier, and hit enter. It will start with AstraCS:cvdPRONUrUUT:…
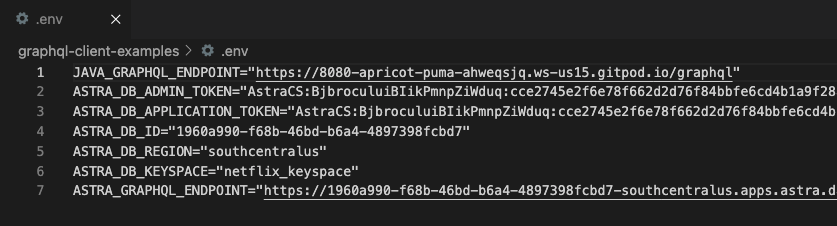
This will add a set of envrionment variables for database authentication to your .env file at the root of workshop-intro-to-graphql/graphql-client-examples. It should look something like this.
✅ Start your React app back up with the following command
netlify dev
✅ Step 9b: Verify data load
At this point your app should be running with a bunch of data displayed in the Shows, Genres, and ReferenceList sections, but notice the ShowsByName section displays “Error :(“
Can you figure out what’s going on here?
Let’s break this down.
-
We just added the database configuration and the
ReferenceListsection is populated which tells us our DB config and graphQL endpoints are configured properly -
In the GraphQL Playground we added a schema for the
reference_listtable and added some data to the table, but we never created a schema for theShowsByNamesection -
If you take a look at the
getShowsAstra.jsscript ingraphql-client-examples/functionsyou can see the graphQL being used to query for data
exports.handler = async function (event) {
const query = `
query getAllShows {
show_by_name {
values {
title
releaseYear
}
}
}
`
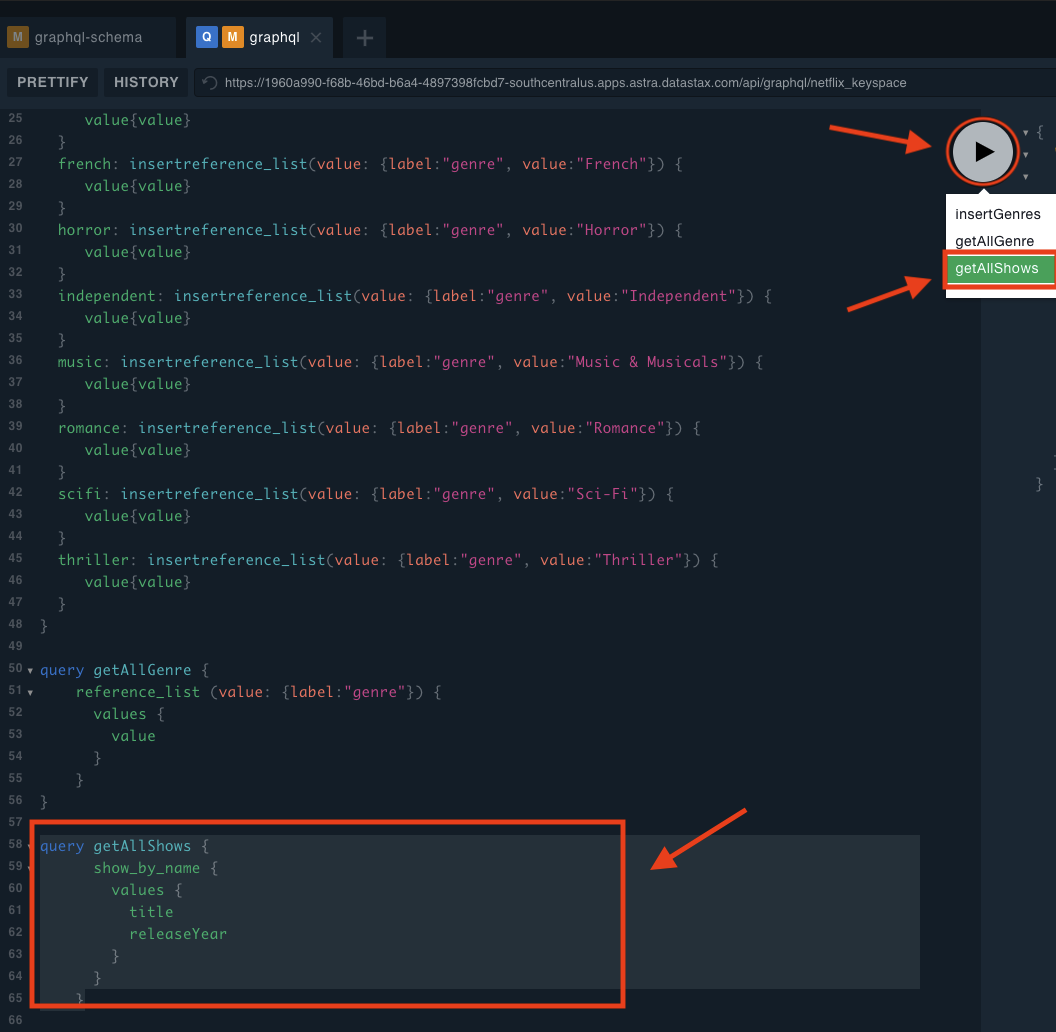
✅ Test this query in the GraphQL Playground graphQL tab
Copy this into the playground and press the “play” button to execute the query. NOTE, you can simply append the query to the end of the list and then choose the query you wish to execute when you hit the “play” button.
query getAllShows {
show_by_name {
values {
title
releaseYear
}
}
}
View Results
Notice what happened here. We have a validation error because there is no schema associated with the query we just executed. GraphQL uses a typed validation system so this is something to expect if a query is malformed, missing a schema, or something along those lines. You will want to control for this in your code.
✅ Step 9c: Create the ShowsByName table with a graphQL mutation to fix the app
Ok, so let’s fix up the schema issue to resolve the error.
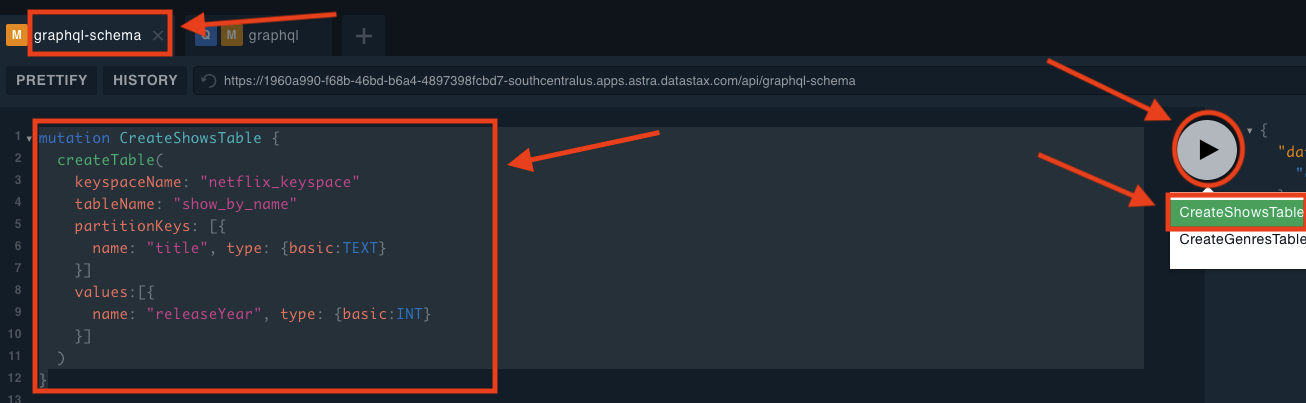
✅ Execute the following mutation in the graph-schema tab of the GraphQL Playground
mutation CreateShowsTable {
createTable(
keyspaceName: "netflix_keyspace"
tableName: "show_by_name"
partitionKeys: [{
name: "title", type: {basic:TEXT}
}]
values:[{
name: "releaseYear", type: {basic:INT}
}]
)
}
✅ Verify result
Once executed you should see a result like this
✅ Add some data
Now, go back to the graphql tab of the GraphQL Playground and add the following mutation
mutation insertShows {
stranger: insertshow_by_name (
value: {
title: "Stranger Things",
releaseYear: 2016}) {
value{title}
}
ozark: insertshow_by_name (
value: {
title: "Ozark",
releaseYear: 2017}) {
value{title}
}
}
✅ Check the result
✅ Finally, refresh your React app
Notice this no longer displays “Error :(“, but now correctly displays the data you just inserted (mutated). It might be fun to add some of your own data to this schema and refresh your page.
Feel free to experiment with a couple more graphQL queries now that you have some data in the table
Notice in this case we are passing a “title” parameter “Ozark” to only return the show values that match that title.
query getOneShow {
show_by_name (value: {title: "Ozark"}) {
values {
title
releaseYear
}
}
}
query getAllShows {
show_by_name {
values {
title
releaseYear
}
}
}
That’s it, you did it! Nice job!
We hope this workshop gave you enough information on GraphQL to be dangerous and start you on a journey to using GraphQL in your own apps. Also, don’t forget to do the HOMEWORK